Which Electrolyte Is Responsible for Carbohydrate Metabolism
Hormone responsible for reabsorption of water and electrolyte to reduce loss of water is. Carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain.

24 2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy Physiology
The players were allocated to two assigned trials.

. The presence of an acidbase or an electrolyte disorder may explain a patients symptoms or may lead to a specific diagnosis. In healthy people it is 44-66 mmoll 70-110 mgdl Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. The groups were matched for subjects age weight height and maximal oxygen uptake Table 1.
Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate lactate glycerol or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. In terms of body functioning six electrolytes are most important. Stores energy that can be used to make ATP 315 seconds of maximal physical effort 0-3 sec 100 ATPCP 10-12 sec 50 ATPCP 50 Carbohydrates 4-6 min 6 ATPCP 94 Carbohydrates 32-40 min 100 Carbohydrates 2-3 hr 75 Carbohydrates 20 Fat 5 Other 5-7 hr 65 Fat 35 Carbohydrates -After creatine.
369 Normal acidbase balance is maintained by the lungs and kidneys. Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation breakdown and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms. Electrolyte imbalances occur when levels of electrolytes are too high or too low which can cause significant derangements.
Electrolytes in living systems include sodium potassium chloride bicarbonate calcium phosphate magnesium copper zinc iron manganese molybdenum copper and chromium. Cortex is further divided into zona glomerulosa zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. AcidBase Balance See Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics p.
This process takes place primarily in the liver during periods of low. Carbon dioxide a by-product of normal metabolism is a weak acid. What are the two glycolytic intermediates that directly link glucose metabolism to the metabolism of triglycerides and thereby link carbohydrate to fat metabolism.
Carbohydrate Metabolism Chlorides metabolism Fructose metabolism Glucose metabolism Glycogen metabolism Humans. Sodium potassium chloride bicarbonate calcium and phosphate. The mechanisms responsible are likely to be the availability of carbohydrate as a substrate for central and peripheral functions.
The lungs are able. A Intake of Potassium. Phosphorous is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates lipids and proteins.
Mechanism of the change in electrolyte and carbohydrate metabolism in the submandibular salivary gland in experimental botulism in rats. Asked Oct 19 2019 in Biology by Purvikumari 340k points class-12. Carbohydrates are central to many essential metabolic pathways.
Complex carbohydrates made up of many monosaccharides pyruvate three-carbon end product of glycolysis and starting material that is converted into acetyl CoA that enters the Krebs cycle salivary amylase digestive enzyme that is found in the saliva and begins the digestion of carbohydrates in the mouth terminal electron acceptor. Figure 2426 Carbohydrate Metabolism. Potassium is the most abundant cation in the ICF of both plants and animals.
Electrolytes are salts that dissolve into positive and negative charges ions and conduct electricity when in water. Magnesium plays a key role in many cell functions including protein carbohydrate and fat metabolism regulation of the parathyroid hormone secretion and maintenance of normal cell membrane functions. Sodium potassium and calcium are not directly responsible for.
I Insulin is the hormone responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates fats and proteins ii Parathyroid hormone is responsible for balancing calcium and phosphate iii Aldosterone is the hormone that controls the Blood pressure. Ingesting carbohydrate-electrolyte CHOE drink carbohydrates 7 sodium 24 mmoll-1 chloride 12 mmoll-1 and potassium 3 mmoll-1 or placebo plain water. To balance the difference in playing.
Increase in content of the fractions responsible for regulation of anaerobic metabolism. Plants synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis allowing them to store. Article in Russian Mikhaĭlov VV Rusanova AG.
Main glucocorticoid hormone responsible for carbohydrate metabolism is. Potassium is also important in carbohydrate metabolism and electron transport since a number of the enzymes in these metabolic pathways are potassium dependent. Metabolism is markedly altered during the growth of cancer manifesting abnormalities in energy carbohydrate lipid and protein metabolism in the water content of tissues the acid-base balance and the concentration of electrolytes and minerals aberrations in vitamin concentrations metabolism and ef-.
Molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates is a sugar level in blood. Effects of carbohydrate-hydration strategies on glucose metabolism sprint performance and hydration during a soccer match simulation in recreational players. IN pp 173-175 Endert E Wolfe RR 1993 Regulation of endogenous fat and Hamilton MT Gonzalez-Alonso J Montain J Coyle EF 1991 carbohydrate metabolism in relation to exercise intensity and Fluid replacement and glucose infusion during exercise prevent duration.
Carbohydrate intake during exercise typically ingested as carbohydrate-electrolyte solutions is also associated with improved performance. Zona glomerulosa is the outermost layer and responsible for production of aldosterone that is a mineralocorticoid which maintains electrolyte and water balance in the body. Carbohydrate metabolism is regulated by glucocorticoids secreted by the zona fasciculata of adrenal cortex.
Conference on in vivo methods. Cations are positively charged ions and anions are negatively charged ions.
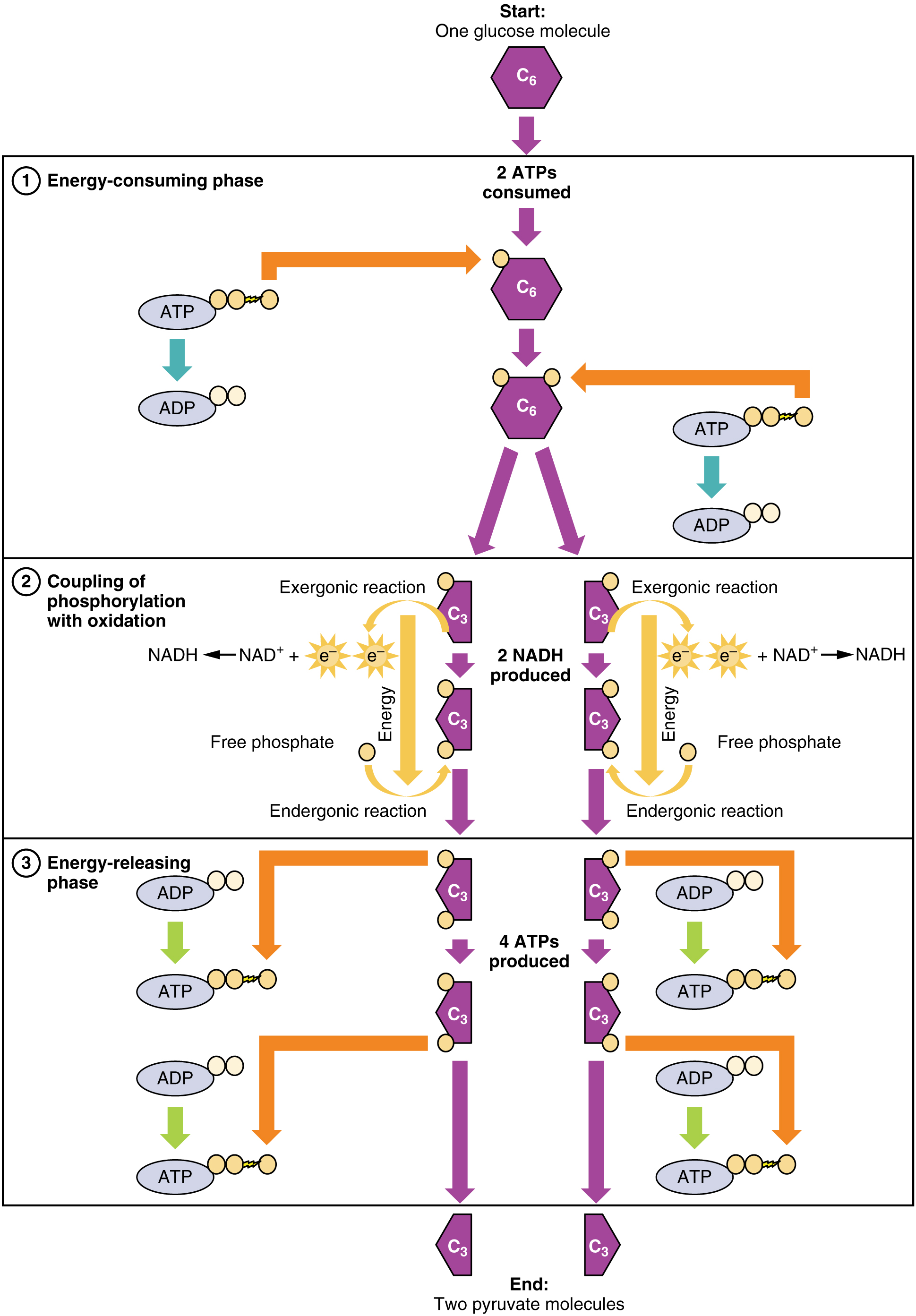
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology

No comments for "Which Electrolyte Is Responsible for Carbohydrate Metabolism"
Post a Comment